Mapping knowledge: Topic analysis of science locates researchers in disciplinary landscape
Mapping knowledge: Topic analysis of science locates researchers in disciplinary landscape

 Image inspired by Tetiana Savaryn/Shutterstock
Image inspired by Tetiana Savaryn/Shutterstock
Mapping knowledge:
Topic analysis of science locates researchers in disciplinary landscape
Yann Renisio
(CNRS, CRIS-Sciences Po)
Radim Hladík
(Center for Science, Technology, and Society Studies, Prague)
Poetics, volume 108, 101950
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poetic.2024.101950
 The study of the compositions of scientific topic portfolios has given us a roadmap to achieve Bourdieu’s goal of overcoming “the distinction […] between the science of scientists and the science of scientific works”.
The study of the compositions of scientific topic portfolios has given us a roadmap to achieve Bourdieu’s goal of overcoming “the distinction […] between the science of scientists and the science of scientific works”.
The study presents a new approach for constructing an epistemological coordinate system that locates individual researchers within the disciplinary landscape of science.
Drawing on a comprehensive national dataset of scientific outputs, the authors build a topic model based on a semantic network of publications and terms derived from textual content comprising titles, abstracts, and keywords. Compositional data transformation applied to the topic model enables a geometric analysis of topics across disciplines.
- The design yields four important results for addressing the gap between knowledge and knowledge-producers. Hierarchical clustering confirms an alignment between traditional disciplinary classification and our empirical, bottom-up topic model.
- Principal component analysis reveals three axes – Culture–Nature, Life–Non-life, and Materials–Methods – that primarily structure this scientific knowledge space.
- The projection of individual researchers via their topic portfolios allows to locate them relationally on these three continuous measures of epistemological distinctions.
- The robustness of our approach is validated by examining the links between researchers’ topic orientation and supplementary variables such as publication practices, gender, institutional affiliations, and funding sources.
This method could inform science policy and evaluation practices, as well as be extended to uncover associations between products and producers in other cultural fields.
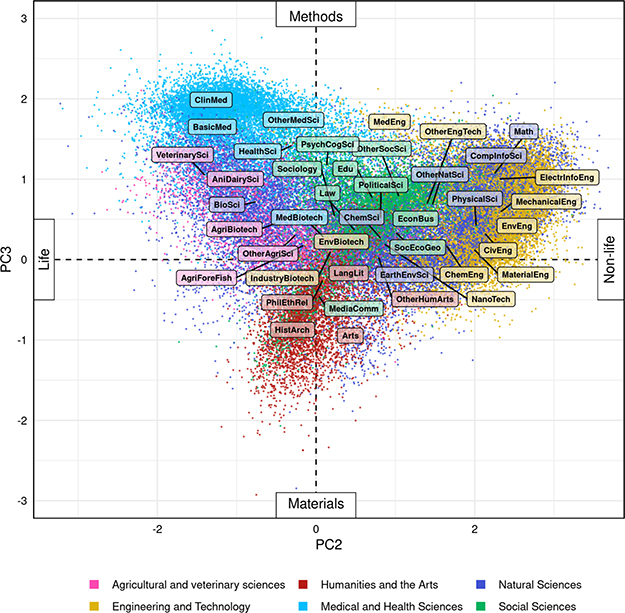
Epistemological coordinates of researchers between Life–Non-life and Materials–Methods oppositions
Each dot corresponds to a projection of an individual topic portfolio onto principal components 2 and 3 in the knowledge space defined by variance of topics across disciplines. N = 58466 of researchers with 5 or more publications. Broad classifications for individuals are denoted by colors, and the mean at the second level of FORD classification is indicated by labels (fig.7 in the paper).